Medical Tests San Antonio, Tx
Laboratory testing
Diabetes Screening & Monitoring:
Diabetes screening and monitoring are essential components of preventive healthcare. Regular screenings help detect diabetes early, allowing for timely intervention and effective management. The screening process typically involves measuring blood glucose levels, with fasting blood sugar and hemoglobin A1c tests being common methods. Fasting blood sugar levels provide a snapshot of glucose concentration after an overnight fast, while hemoglobin A1c reflects average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months.
Monitoring diabetes involves regular check-ups, lifestyle modifications, and medication adherence. Patients should maintain a balanced diet, engage in regular physical activity, and monitor blood sugar levels as prescribed by healthcare professionals. Annual eye exams and kidney function tests are crucial to identify potential complications. Early detection and consistent monitoring empower individuals to take control of their condition and prevent complications such as neuropathy, retinopathy, kidney diseases and cardiovascular issues.

High Cholesterol Screening & Monitoring:
High cholesterol screening and monitoring are vital for cardiovascular health. Elevated cholesterol levels contribute to atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Screening involves a fasting lipid panel test, which measures total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and triglycerides. Optimal cholesterol levels vary, but healthcare providers often recommend maintaining low LDL and high HDL levels.
Monitoring involves lifestyle modifications and, in some cases, medication. Adopting a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding tobacco products are essential for managing cholesterol levels.
Regular follow-up screenings are crucial to assess the effectiveness of interventions and adjust treatment plans accordingly. Individuals with high cholesterol should be vigilant about maintaining a healthy lifestyle and attending regular medical check-ups to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.
Thyroid Screening & Monitoring:
Thyroid screening and monitoring are integral to maintaining hormonal balance and overall well-being. The thyroid gland regulates metabolism, energy production, hair & nail health and body temperature. Screening involves blood tests measuring thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), free thyroxine (T4), and triiodothyronine (T3) levels. Abnormalities in these levels may indicate hypo- or hyperthyroidism, conditions that can affect energy levels, weight, and mood. Thyroid screenings can also detect conditions such as Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
Monitoring thyroid function involves regular follow-up tests and adjustments to medication if necessary.
Patients with thyroid disorders should collaborate closely with healthcare providers to optimize treatment. Lifestyle factors such as stress management, adequate sleep, and a balanced diet also play a role in thyroid health. Early detection and consistent monitoring empower individuals to manage thyroid conditions effectively and prevent complications.
Anemia Screening & Monitoring:
Anemia screening and monitoring are crucial for identifying and managing deficiencies in red blood cells or hemoglobin. Common causes include nutritional deficiencies, chronic diseases, bleeding and genetic factors. Screening involves a complete blood count (CBC) to assess red blood cell levels and hemoglobin concentration. Low levels may indicate anemia, leading to symptoms like fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
Monitoring anemia involves identifying and addressing the underlying cause. Treatment may include dietary changes, iron supplementation, identifying any blood loss or addressing chronic conditions contributing to anemia. Regular follow-up blood tests help assess the effectiveness of interventions and adjust treatment plans accordingly. Individuals with anemia should work closely with healthcare providers to address the root cause and optimize their overall health.
Urine Testing – Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs):
Urine testing is a crucial diagnostic tool, especially for detecting urinary tract infections (UTIs). UTIs can cause discomfort, pain, and, if left untreated, may lead to more severe complications. Urine tests typically involve analyzing a sample for the presence of bacteria, white blood cells, and other abnormalities.
Early detection of UTIs is essential for prompt treatment with antibiotics. Symptoms such as frequent urination, pain or burning during urination, and cloudy or strong-smelling urine may indicate a UTI. Routine urine testing is also essential for monitoring kidney function and detecting conditions like kidney stones or diabetes. Hydration, good personal hygiene, and prompt medical attention for UTIs contribute to overall urinary tract health.


Liver, Pancreas, and Kidney Laboratory Evaluation:
Laboratory evaluation of the liver, pancreas, and kidneys is vital for assessing organ function and detecting potential issues. Liver function tests measure enzymes and proteins indicative of liver health. Pancreatic function tests such as amylase and lipase assess the pancreas’s ability to produce digestive enzymes and insulin. Kidney function tests, including blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine levels, help evaluate renal health.
Monitoring these organs is crucial for identifying conditions such as liver disease, pancreatitis, or kidney dysfunction. Lifestyle factors, including alcohol consumption and dietary choices, can significantly impact these organs.
Regular follow-up tests, combined with a healthy lifestyle, contribute to the prevention and early detection of organ-related issues. Consultation with healthcare professionals is essential for interpreting results and developing personalized care plans.
Monitoring of Certain Cardiac and Seizure Medications:
Monitoring certain cardiac and seizure medications is essential for ensuring efficacy and preventing potential side effects. Regular assessments involve blood tests to measure medication levels, ensuring they remain within therapeutic ranges. For cardiac medications, such as anti-arrhythmics or blood thinners, maintaining appropriate levels is crucial for preventing blood clots, bleeding or irregular heart rhythms.
Seizure medications require careful monitoring to prevent seizures while minimizing side effects. Blood tests help determine drug levels, allowing healthcare providers to adjust dosages as needed.
Close collaboration between patients and healthcare professionals is essential for effective medication management. Regular check-ups and open communication about any concerning symptoms or changes in health contribute to optimal medication outcomes and overall well-being.
Radiographic Testing
Head and Skull X-rays:
Head and skull X-rays are diagnostic imaging procedures that capture detailed images of the bones in the head and skull. These X-rays are commonly used to assess injuries, fractures, or abnormalities in the skull, such as suspected head trauma or cranial fractures. They play a crucial role in identifying potential issues related to the skull, brain, and facial structures. These X-rays are non-invasive and provide rapid results, aiding healthcare professionals in prompt diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Head and skull X-rays are valuable tools for assessing trauma, fractures, and abnormalities in the cranial region.
- They are often used in emergency settings to quickly evaluate injuries after accidents or head trauma.
- The procedure is safe, non-invasive, and typically involves minimal radiation exposure.
- Rapid results facilitate swift medical intervention and decision-making.

Facial, Orbits, and Sinus X-rays:
Facial, orbits, and sinus X-rays are imaging techniques designed to capture detailed images of the face, eye sockets (orbits), and sinus cavities. These X-rays assist healthcare professionals in diagnosing issues such as facial fractures, sinus infections, or abnormalities in the orbital region. The procedure is swift, non-invasive, and aids in creating a comprehensive picture of the facial structures, facilitating accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
- These X-rays are instrumental in assessing facial injuries, orbital fractures, and sinus conditions.
- They provide detailed images that help healthcare professionals identify the extent and nature of facial abnormalities.
- The procedure is generally quick, with minimal discomfort for the patient.
- Rapid results contribute to timely medical decision-making.
Chest X-rays:
Chest X-rays are diagnostic tools that capture images of the chest, including the heart, lungs, and surrounding structures. These X-rays are commonly used to detect and evaluate conditions such as pneumonia, lung diseases, heart abnormalities, or chest injuries. Chest X-rays are essential in routine medical examinations, providing valuable insights into respiratory and cardiovascular health.
- Chest X-rays are fundamental for detecting and monitoring various respiratory and cardiovascular conditions.
- They are often used in routine check-ups, pre-surgical assessments, and emergency situations.
- The procedure is quick and involves minimal radiation exposure.
- Chest X-rays contribute to the early diagnosis and treatment of chest-related disorders.

Clavicle, Sternum, and Rib X-rays:
Clavicle, sternum, and rib X-rays are imaging procedures that focus on capturing detailed images of the collarbone (clavicle), breastbone (sternum), and ribs. These X-rays are commonly employed to diagnose fractures, injuries, or abnormalities in these skeletal structures. The imaging process is efficient, providing healthcare professionals with valuable information to assess and manage injuries to the chest and upper torso.
- These X-rays play a crucial role in diagnosing fractures and injuries to the clavicle, sternum, and ribs.
- They are often employed after trauma, accidents, or sports-related injuries in the chest area.
- The procedure is non-invasive and yields rapid results.
- Accurate imaging aids in effective treatment planning and rehabilitation.
Cervical, Thoracic, and Lumbar X-rays:
Cervical, thoracic, and lumbar X-rays are diagnostic imaging techniques used to visualize the vertebrae in the neck (cervical), upper back (thoracic), and lower back (lumbar) regions. These X-rays help identify spinal abnormalities, fractures, or degenerative conditions affecting these areas. The imaging process is essential for assessing spine health and guiding medical interventions, such as spinal surgeries or therapeutic interventions.
- These X-rays provide detailed images of the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine for diagnostic purposes.
- They are commonly used to evaluate spinal injuries, degenerative conditions, or abnormalities.
- The procedure is non-invasive, quick, and involves minimal radiation exposure.
- Accurate imaging aids in determining appropriate treatment plans for spinal conditions.

Abdominal X-rays:
Abdominal X-rays are diagnostic tools used to capture images of the organs and structures in the abdominal cavity such as the bowels, kidneys, ureters and bladder. These X-rays assist healthcare professionals in identifying issues such as gastrointestinal obstructions, abdominal injuries, or abnormalities in organ positioning. Abdominal X-rays are valuable in emergency situations, routine check-ups, and pre-surgical assessments.
- Abdominal X-rays provide insights into the condition of abdominal organs and structures.
- They are commonly used to identify gastrointestinal issues, obstructions, and abdominal injuries.
- The procedure is non-invasive and generally quick, with minimal patient discomfort.
- Rapid results contribute to timely medical decision-making.
Extremities: Arms, Wrist, Hands, Fingers, Legs, Ankles, Feet, Toes:
Extremity X-rays encompass imaging of various body parts, including arms, wrists, hands, fingers, legs, ankles, feet, and toes. These X-rays are employed to diagnose fractures, dislocations, or abnormalities in the bones and joints of the extremities such as arthritis. The imaging process is versatile, aiding in the assessment of injuries from accidents, sports-related trauma, or degenerative conditions affecting the limbs.
- Extremity X-rays are versatile and cover a range of body parts, facilitating the diagnosis of arthritis and limb injuries.
- The procedure is non-invasive and provides rapid results.
- The procedure is non-invasive, quick, and involves minimal radiation exposure.
- Accurate imaging supports effective treatment planning for limb injuries and conditions.

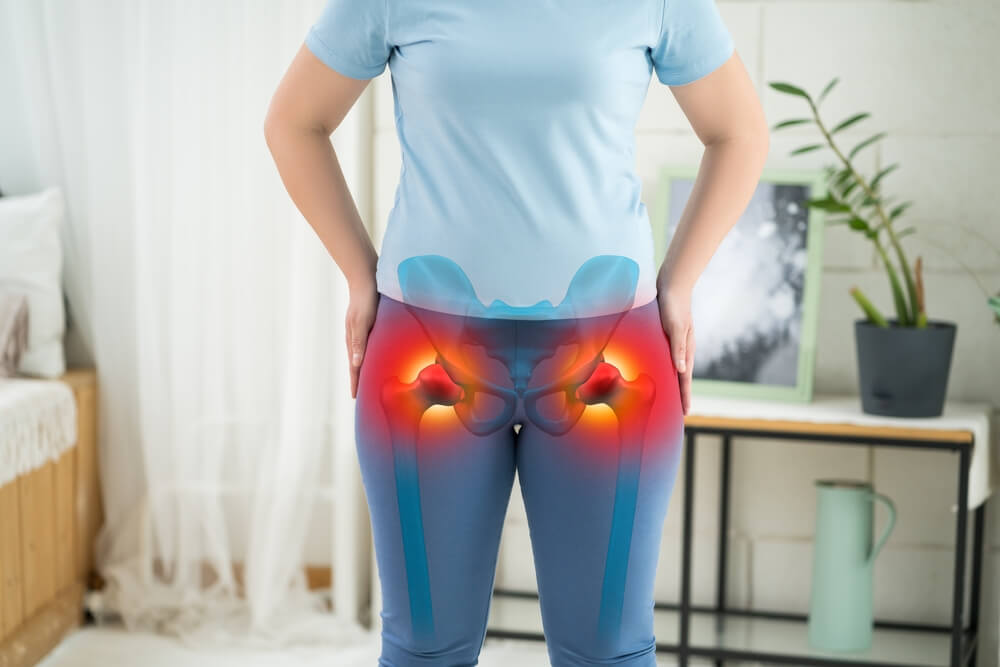
Hip and Pelvic X-rays:
Hip and pelvic X-rays focus on capturing detailed images of the hip joint and pelvic bones. These X-rays are instrumental in diagnosing hip fractures, arthritis, or congenital abnormalities in the pelvic region. The imaging process aids healthcare professionals in assessing hip joint health and guiding interventions such as joint replacements or surgical procedures.
- Hip and pelvic X-rays are essential for diagnosing hip joint conditions, fractures, and pelvic abnormalities.
- They play a crucial role in orthopedic assessments and pre-surgical planning.
- The procedure is non-invasive, and results are typically obtained promptly.
- Accurate imaging supports effective decision-making in the management of hip and pelvic issues.
Bone Density Test (DEXA) with Same-Day Results:
Bone density tests, also known as DEXA scans, are specialized imaging procedures designed to measure bone mineral density. These tests are crucial for assessing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. The DEXA scan provides detailed information about bone health, and with same-day results, healthcare professionals can promptly initiate preventive measures or treatment plans.
- DEXA scans are key for assessing bone mineral density and identifying osteoporosis risk.
- Same-day results enable timely interventions, such as lifestyle changes or medication.
- The procedure is non-invasive, involves minimal radiation exposure, and is painless.
- Regular DEXA scans are usually performed every 2 years and essential for monitoring bone health, especially in postmenopausal women and older adults.

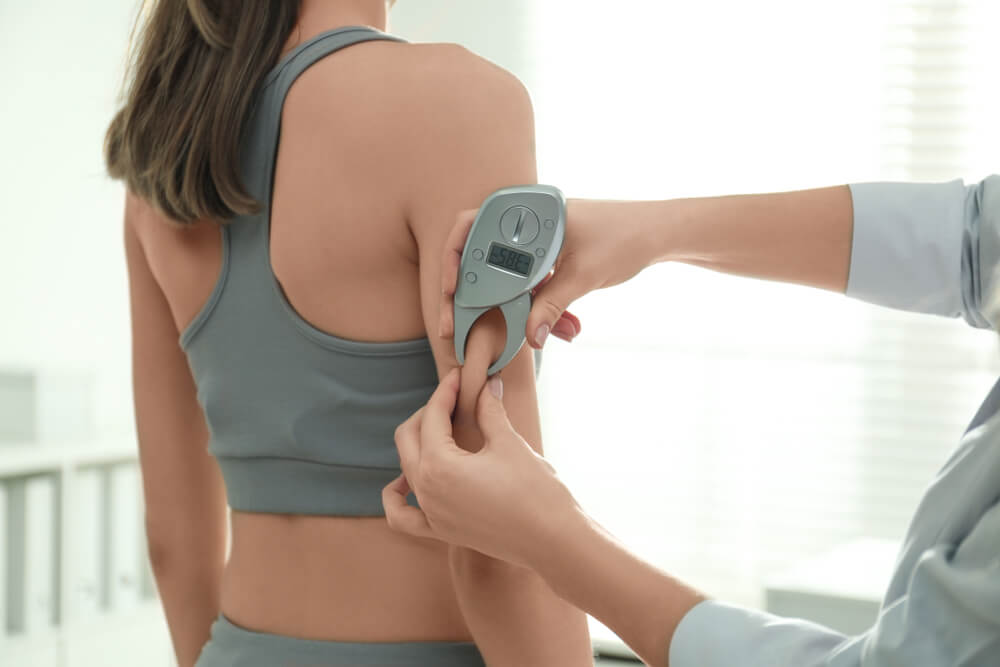
Body Composition to Test Body Fat Percentage, with Same-Day Results (350 lbs Weight Limit):
Body composition testing measures the percentage of body fat and lean muscle mass. This information is valuable for assessing overall health and fitness. With same-day results, individuals can promptly adjust their lifestyle habits based on the findings. The test has a weight limit of 350 lbs, ensuring inclusivity for a wide range of individuals.
- Body composition testing provides insights into body fat percentage and overall fitness levels.
- Same-day results empower individuals to make timely adjustments to their lifestyle.
- The procedure is non-invasive, quick, and suitable for individuals up to 350 lbs.
- Regular body composition assessments support health and wellness goals.
12 Lead ECG with Interpretation:
A 12 Lead ECG (Electrocardiogram) is a diagnostic test that records the electrical activity of the heart from multiple angles. This test is crucial for detecting cardiac abnormalities, such as arrhythmias or ischemic heart disease. The ECG provides valuable information about the heart’s rhythm and helps healthcare professionals interpret and diagnose various heart conditions.
- A 12 Lead ECG is a standard test for evaluating the electrical activity of the heart.
- It is instrumental in diagnosing arrhythmias, heart attacks, and other cardiac issues.
- The procedure is non-invasive, quick, and essential in emergency and routine cardiac assessments.
- Interpretation by healthcare professionals ensures accurate diagnosis and appropriate interventions.

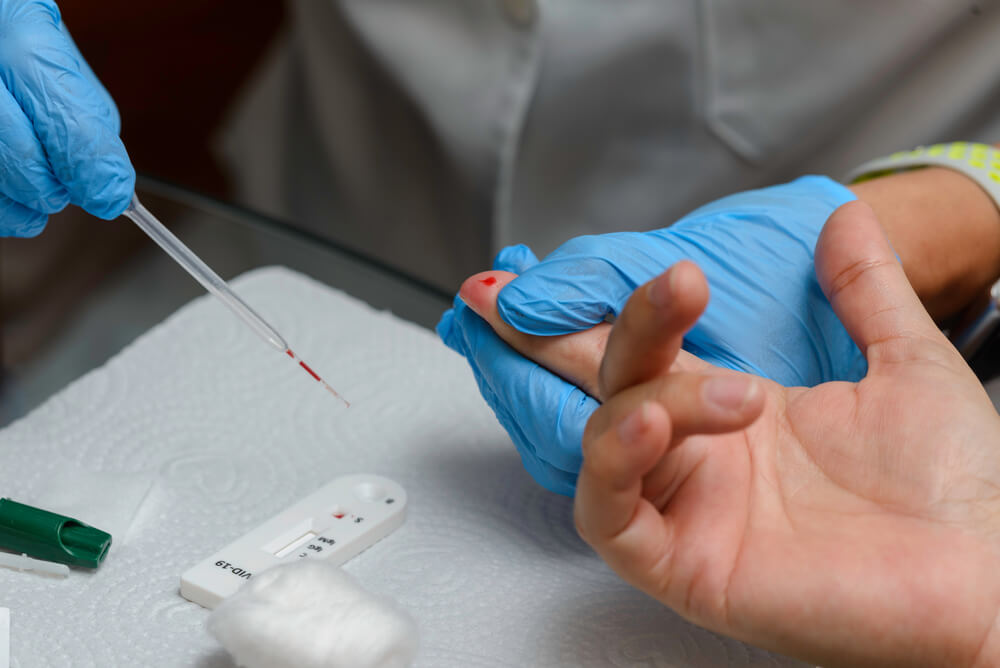
Rapid Strep Testing:
Rapid Strep testing is a quick diagnostic procedure used to detect the presence of streptococcal bacteria in the throat. This test is essential for diagnosing strep throat, a bacterial infection that requires prompt treatment with antibiotics. The rapid nature of the test allows for swift diagnosis and initiation of appropriate medical interventions.
- Rapid Strep testing is a fast and reliable method for diagnosing strep throat.
- Results are obtained quickly, enabling timely administration of antibiotic treatment.
- The procedure is minimally invasive and well-tolerated by patients.
- Early diagnosis and treatment help prevent the spread of streptococcal infections.
COVID-19/Influenza/RSV Testing:
Testing for COVID-19, Influenza, and Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is crucial for identifying and managing respiratory infections. These tests are particularly important in the context of public health, enabling prompt isolation and treatment of affected individuals. Rapid results from these tests take approximately 35 minutes and aid in effective disease control and prevention.
- COVID-19/Influenza/RSV testing is essential for diagnosing respiratory infections.
- Rapid results contribute to timely isolation and treatment measures.
- Testing is critical for public health, helping prevent the spread of contagious diseases.
- Individuals with respiratory symptoms should undergo testing to ensure appropriate medical care.