Pulmonary Health
Unveiling the Secrets of Pulmonary Health: Understanding and Managing Respiratory Conditions:
Welcome to a diversified guide on pulmonary health, where we delve into the world of common respiratory illnesses. The pulmonary system plays a vital role in sustaining breathing and life, and understanding its various facets is crucial for maintaining optimal health. We’ll explore important categories related to pulmonary health, focusing on conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pneumonia, bronchitis, obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), pulmonary embolus (PE), and seasonal allergic rhinitis.
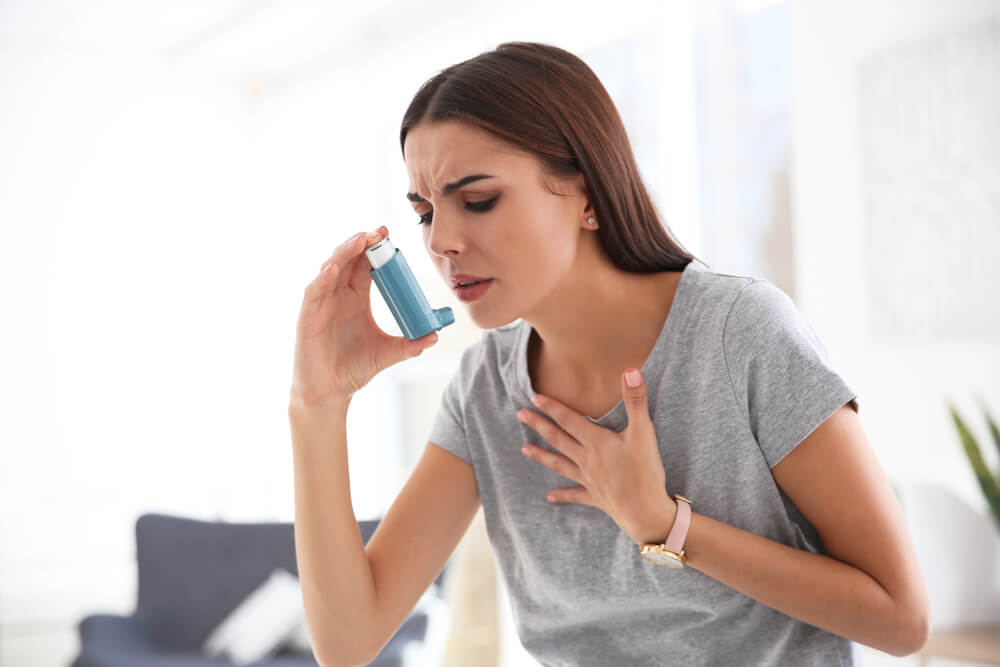

Asthma:
Asthma is a common respiratory condition that affects millions of people worldwide, across all ages, races, sexes and socioeconomic levels. Wheezing is a hallmark symptom that can occur due to narrowed airways caused by bronchospasms, making breathing very difficult, sometimes leading to status asthmaticus and even death. While the lungs can appear structurally normal, environmental triggers such as allergens and pollutants play a significant role in episodic exacerbations. Asthma is often diagnosed by using a combination of patient history, physical examinations, chest x-rays and pulmonary function tests (PFT’s).
Effective asthma management and treatment involves identifying triggers, implementing lifestyle changes, and using prescribed medications. Regular use of inhalers, bronchodilators, and anti-inflammatory drugs are commonly prescribed to control symptoms & exacerbations and improve overall lung function.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD):
COPD is a group of lung diseases to include chronic bronchitis and emphysema. It poses a significant health threat globally, especially to the elderly population. A long-standing smoking history can be a significant risk factor for developing this debilitating lung disease. leading to persistent coughing, shortness of breath, and reduced lung function. Pulmonary function tests (PFT’s) are often used to determine disease severity. For those living with COPD, lifestyle modifications and medication adherence are paramount. In severe cases, supplemental oxygen therapy may be necessary to alleviate breathing difficulties and improve oxygenation.
Smoking cessation remains the most effective preventive measure and can significantly slow down the progression of the disease.
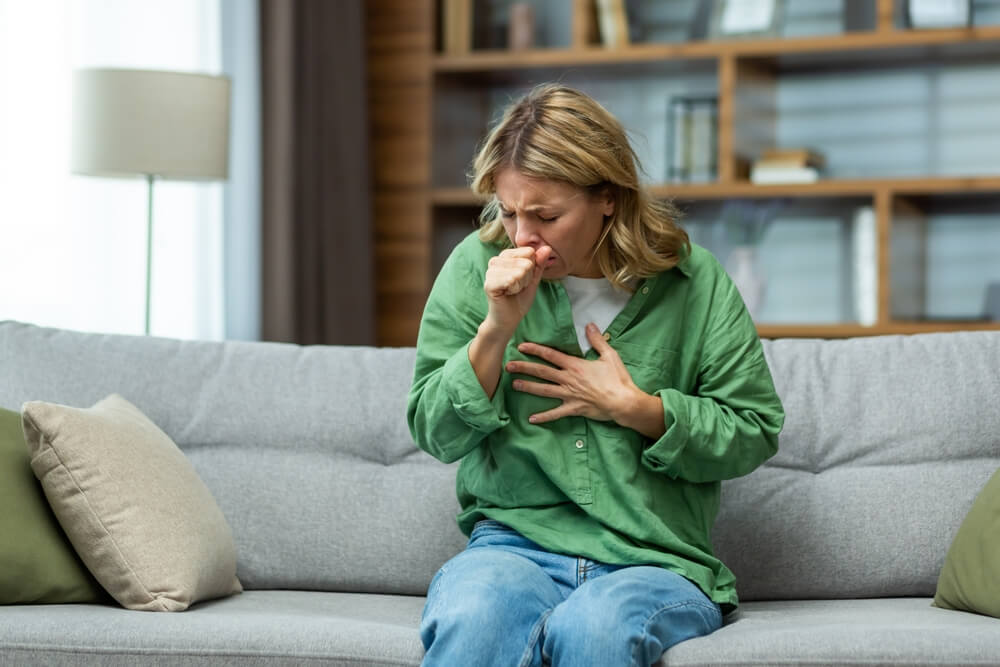

Pneumonia:
Pneumonia is an infection affecting the airways in the lungs and can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Common symptoms include cough, sputum production, fever & chills, and difficulty breathing, making prompt diagnosis and treatment critical. It is the leading cause of infection-related deaths in the United States.
Antibiotics, antivirals, or antifungal medications, depending on the cause, are prescribed to treat pneumonia. Supportive care to include frequent bronchodilators and supplemental oxygen therapy are sometimes necessary, especially in the inpatient setting. Vaccination against bacterial and viral agents, good hygiene practices, and a healthy lifestyle to include avoidance of tobacco smoke contribute to preventing pneumonia.
Bronchitis:
Bronchitis is characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes and leads to persistent coughing, mucus production, and chest discomfort. It can be acute or chronic, with viral infections often triggering the former and prolonged exposure to irritants causing the latter.
Treatment involves relieving symptoms and addressing underlying causes. Rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications to alleviate cough and fever are common for acute bronchitis. Chronic bronchitis management may require long-term bronchodilators, inhaled steroids, and lifestyle changes.
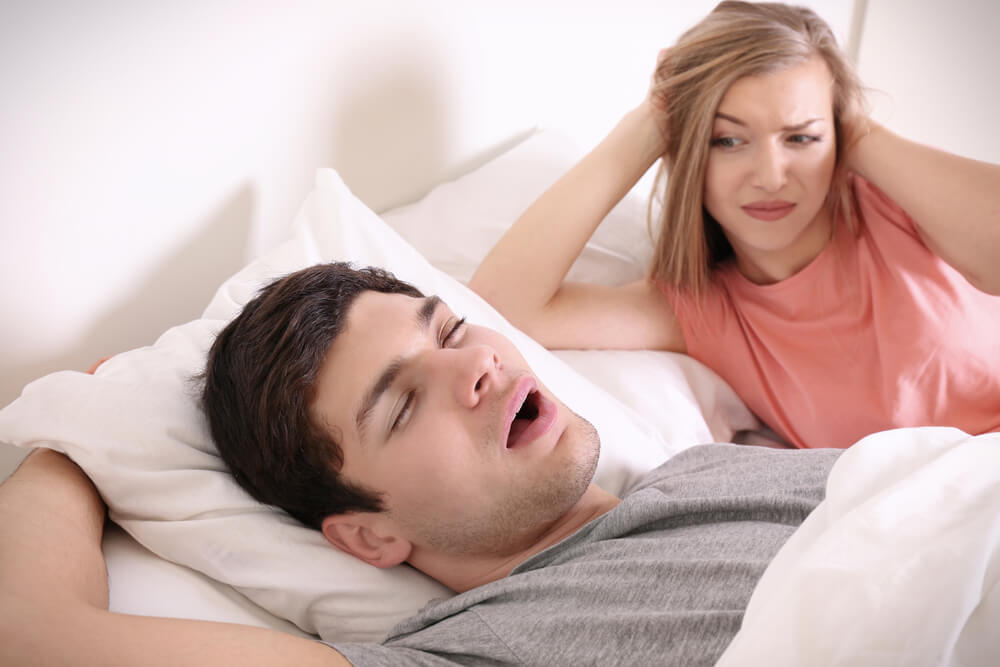


Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA):
OSA is a sleep disorder characterized by long and frequent pauses in breathing during sleep, often accompanied by loud snoring and daytime somnolence. Obesity, genetics, and structural abnormalities of the throat and neck can contribute to its development, impacting both sleep quality and overall health. Untreated OSA can lead to other serious health issues to include uncontrolled hypertension (high blood pressure) and cardiac arrhythmias.
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy is a standard treatment for OSA, providing a steady flow of air to splint airways open. Lifestyle changes, such as weight management, positional therapy and complemental medical interventions ensure a more restful sleep.
Pulmonary Embolus (PE):
PE occurs when blood clots, usually originating in the legs, travel to the lungs, posing a serious and potentially life-threatening condition. Symptoms include sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, and rapid heart rate.
Prompt identification and medical intervention is critical for the treatment of PE. Anticoagulant medications are often prescribed to prevent further clot formation. In severe cases, procedures like thrombectomy may be necessary to remove large clots and restore ventilation and oxygenation.
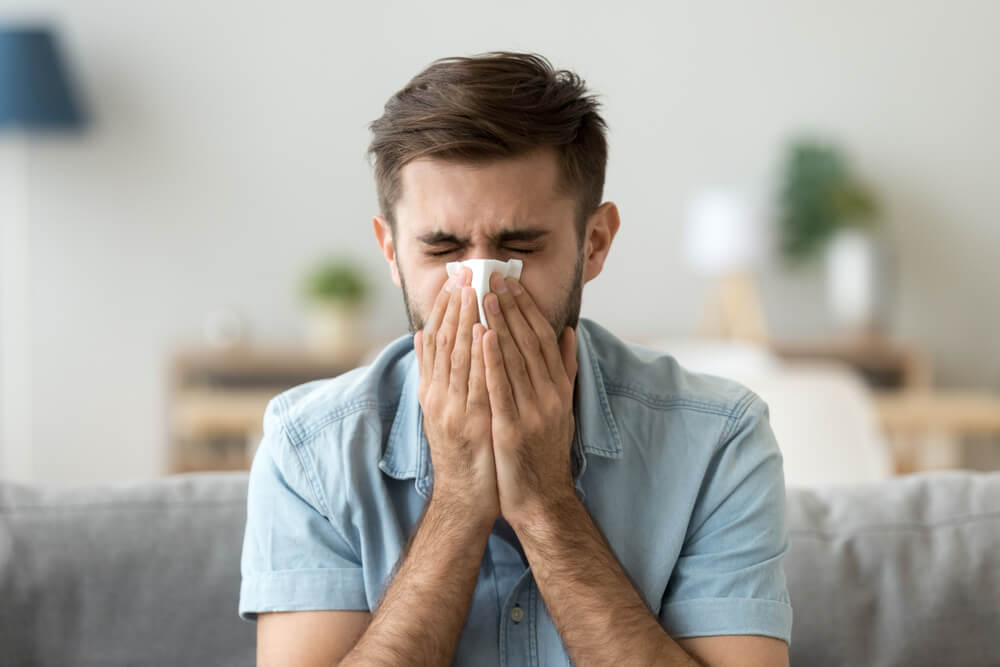

Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis:
Seasonal allergic rhinitis is an allergic reaction to airborne allergens such as ragweed, mountain cedar or mold. It manifests with symptoms such as sneezing, nasal congestion, and itchy eyes, affecting the quality of life, especially during specific seasons.
Antihistamines, nasal corticosteroids, and decongestants are commonly used to manage symptoms. Allergen avoidance, such as staying indoors during high pollen seasons, can significantly reduce the impact of seasonal allergic rhinitis on respiratory health.
Discover Juan S. Pico in San Antonio, TX:
Located in the heart of San Antonio, Juan S. Pico is your dedicated partner in pulmonary health. Our team combines expertise with a human touch, ensuring that each patient receives personalized care. Whether you’re dealing with asthma, COPD, pneumonia, bronchitis, sleep apnea, pulmonary embolism, or allergic rhinitis, trust Juan S. Pico for expert guidance and support. Breathe easy – we’ve got your pulmonary health covered.

